As one of the core components of fluid control systems, valves play a crucial role. A wide variety of valves are extensively used in various fields such as industry, chemical engineering, construction, and civil applications, becoming essential "guardians" in fluid systems. They accurately control the direction, flow rate, and pressure of the medium, ensuring the efficient operation of the entire system. We can't help but ask, what types of valves are there? How do different types of valves showcase their characteristics and advantages in various application scenarios? This article will delve into the diverse classifications and applications of valves, uncovering the mysteries of this critical component.
Basic Classification of Valves
From the perspective of basic functions and driving methods, valves can be divided into two major categories: automatic valves and actuated valves.
Automatic Valves
As the name suggests, automatic valves rely on the flow characteristics of the fluid (liquid or gas) itself to automatically open and close, without the need for external driving forces. These valves can automatically adjust their opening or closing state based on the fluid's pressure changes, flow direction, flow rate, and other characteristics. For example, a check valve is a typical automatic valve that only allows fluid to flow in one direction. When the fluid flows in the reverse direction, the valve will automatically close to prevent backflow. Automatic valves have a simple design and compact structure, making them widely used in many scenarios that do not require frequent adjustments, ensuring the safety and reliability of the system.
Actuated Valves
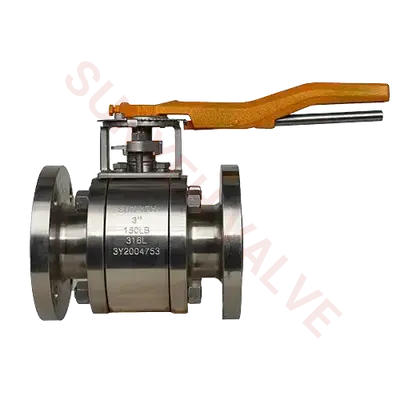
Unlike automatic valves, actuated valves require external forces for control, usually relying on manual, mechanical, or electrical equipment to achieve opening, closing, or flow regulation. actuated valves are suitable for systems requiring more precise and stable fluid control. Typical types include gate valves, globe valves, butterfly valves, and ball valves. These valves can accurately control the flow and pressure of the medium and are core devices in modern fluid control systems.
Subtypes of actuated valves
Actuated valves can be further categorized based on their driving methods into manual valves, electric valves, hydraulic valves, and air actuated valves. Each driving method endows the valve with different characteristics to meet various working conditions.
Manual Valves
Manual valves are the most common type of actuated valves. Using devices such as handwheels, handles, or levers, operators manually control the opening and closing states of the valve. Manual valves have a simple structure, are relatively low-cost, and are easy to operate without additional power support. Therefore, they are widely used in small pipelines or low-frequency operation scenarios within fluid systems. However, due to the need for manual operation, the control precision of manual valves is limited, making them unsuitable for scenarios requiring remote or automated control.
Electric Valves
Electric valves utilize motors or other electrical devices to drive the opening, closing, and regulation of the valve, featuring quick response speeds and high control precision. Electric valves perform excellently in systems requiring frequent adjustments or remote operations, such as air conditioning, fire protection, and automated production lines. Their precise control capability makes them play an essential role in modern automated control systems, especially suitable for accurate fluid control in industrial processes.
Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic valves are driven by liquids like water or oil and are typically used in high-pressure and high-flow scenarios. Due to the stability and strong thrust of hydraulic drive systems, hydraulic valves perform outstandingly in large fluid control systems, capable of withstanding higher working pressures. They are particularly prominent in the energy, petrochemical, and power industries. Hydraulic valves have excellent regulation performance and high reliability, making them suitable for continuous operation environments.
Air Actuated Valves
Air actuated valves are driven by compressed air and feature a simple structure and rapid action, making them suitable for scenarios requiring quick responses. Air actuated valves are widely used in automated factories, production lines, and the pharmaceutical and food industries because of their fast opening and closing speeds, making automatic control easy to achieve. Additionally, due to the high explosion-proof performance of air actuated systems, air actuated valves are the ideal choice for flammable and explosive environments.
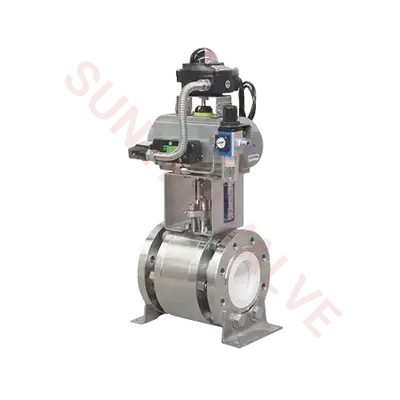
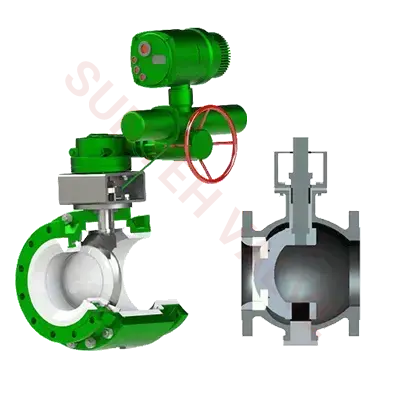
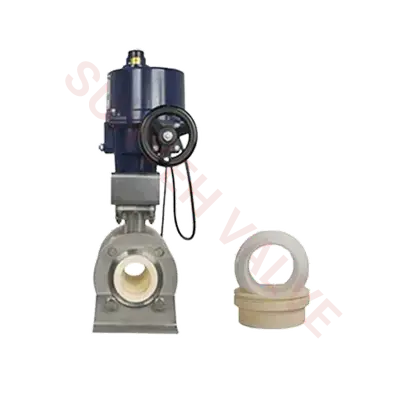
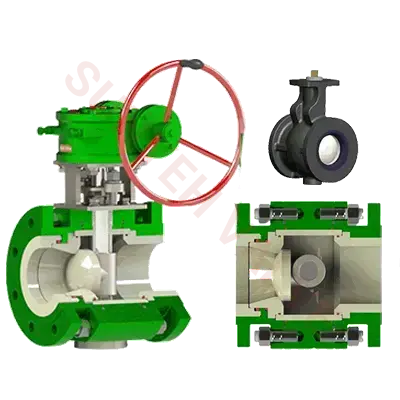
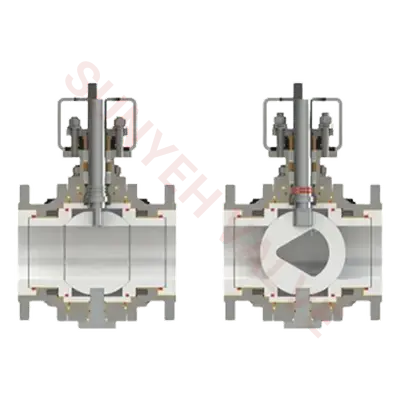
Sunyeh Ceramic Actuated Valves — High-End Wear-Resistant Solutions
In harsh conditions involving high wear and high corrosion, Sunyeh's ceramic actuated valves demonstrate excellent durability and reliability. These valves combine advanced actuation technology with high-hardness ceramic materials. The wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant ceramic lining handles extreme operating environments, ensuring system sealing and stability while providing a long service life. Ceramic actuated valves are easy to operate, offer excellent explosion-proof performance, mature execution schemes, and fast response speeds, making them particularly suitable for fluid control scenarios with strong acidic or alkaline media or high solid particle content. They are a reliable choice for high-standard working conditions.
In conclusion, as the "gatekeepers" in fluid systems, valves play a critical regulatory role. From automated valves to the diverse designs of actuated valves, various types of valves, with their unique driving methods and material characteristics, provide diverse solutions to meet the different needs of modern industry. In the future, with the development of technology and increasing demands for more efficient and reliable fluid control, valve technology will continue to innovate, offering smarter and more precise control methods for various industries.
 English
English