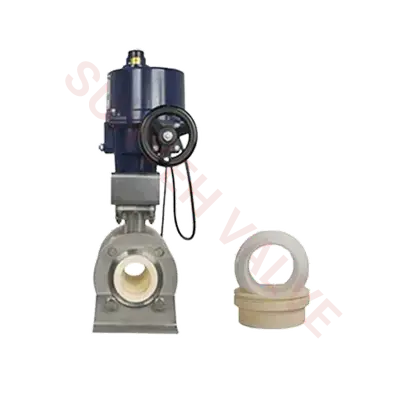
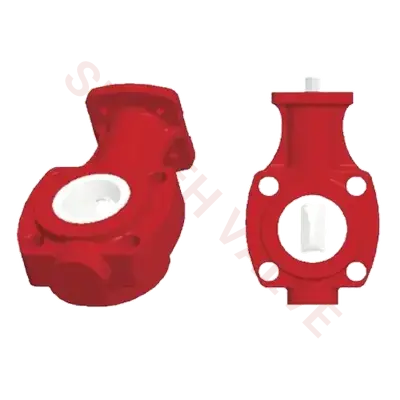
Ball valves are essential components in fluid control systems, offering reliable shut-off capabilities and efficient flow control. Traditionally, metal ball valves have been widely used across various industries due to their durability and versatility. However, the emergence of ceramic ball valves has introduced new possibilities for applications requiring superior resistance to corrosion, wear, and harsh environments.

Material Composition and Properties
Metal ball valves are typically constructed from materials such as stainless steel, brass, or bronze, offering good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. On the other hand, ceramic ball valves utilize advanced ceramic materials like alumina (aluminum oxide) or zirconia (zirconium oxide), known for their exceptional hardness, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. Ceramic valves also exhibit low friction, reducing wear and improving longevity.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
One of the most significant advantages of ceramic ball valves is their superior resistance to corrosion. In corrosive environments containing acids, alkalis, or abrasive substances, ceramic valves outperform metal valves by maintaining their integrity and functionality over extended periods. This resistance to corrosion ensures minimal maintenance requirements and prolonged service life, making ceramic valves a preferred choice for challenging applications.
Performance in High-Temperature and High-Pressure Environments
Ceramic ball valves excel in high-temperature and high-pressure applications where traditional metal valves may fail. Withstanding extreme temperatures and pressures without compromising performance, ceramic valves offer reliable operation in environments such as chemical processing, power generation, and petrochemical industries. Their ability to maintain tight sealing and structural integrity under harsh conditions ensures uninterrupted flow control and process efficiency.
Cost Considerations and Application Specificity
While ceramic lined ball control valves offer numerous advantages, including superior corrosion resistance and durability, they may come at a higher initial cost compared to metal valves. Therefore, the selection of valve materials should consider factors such as application requirements, operating conditions, maintenance costs, and lifecycle considerations. For applications where corrosion, wear, and temperature extremes are significant concerns, the long-term benefits of ceramic valves may outweigh the initial investment.
In conclusion, ceramic ball valves represent a compelling alternative to traditional metal ball valves, offering unparalleled resistance to corrosion, wear, and harsh environments. By understanding the differences in material composition, properties, and performance characteristics, industries can make informed decisions when selecting ball valves for their fluid control systems. Whether in chemical processing, oil and gas, or manufacturing applications, ceramic ball valves demonstrate their superiority in demanding operating conditions, ensuring reliable and efficient flow control.
 en
en  es
es  ru
ru  ar
ar  tr
tr  id
id